RGBDNeRF: Neural Radiance Fields from Sparse RGB-D Images
for High-Quality View Synthesis
Yu-Jie Yuan1,2
Yu-Kun Lai3
Yi-Hua Huang1,2
Leif Kobbelt4
Lin Gao1,2†
† Corresponding author
1 Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
3 Cardiff University
4RWTH Aachen University
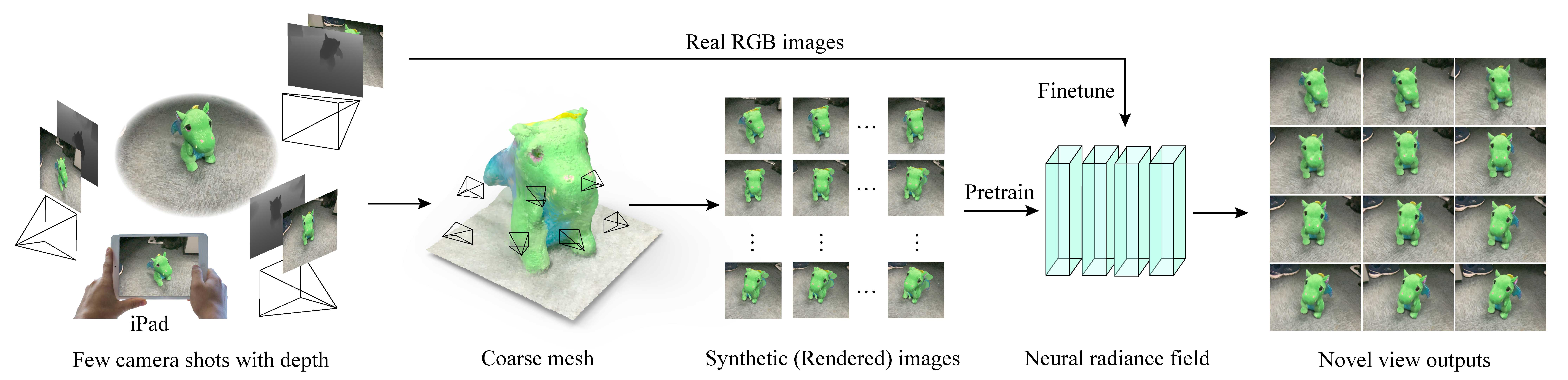
Figure 1: We propose a novel NeRF (Neural Radiance Field) framework that uses sparse RGB-D images to synthesize novel view images. These RGB-D images are acquired using consumer devices such as an iPad Pro. We first use the rendered images of the reconstructed mesh to pre-train the NeRF network, and then use the real captured images to fine-tune the network to synthesize realistic images from novel views.
Abstract
Recently proposed neural radiance fields (NeRF) use a continuous function formulated as a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to model the appearance and geometry of a scene, which enables realistic synthesis of novel views, even for scenes with view dependent appearance. The technique becomes popular, with many follow-up works that extend it in different ways. However, a fundamental restriction of such methods is that they require a large number of images captured from densely placed views for high-quality synthesis, and may produce degraded results when the number of captured views is insufficient. To address this, we propose a novel NeRF-based framework capable of high-quality view synthesis using only sparse RGB-D images, which can be easily captured using cameras and LiDAR sensors on consumer devices, such as an iPad Pro, without additional effort from the user. The captured RGB-D images are first used to reconstruct rough geometry of the scene, and a sufficient number of close-to-real renderings can then be generated for pre-training the network, along with precise camera parameters. The network is then fine-tuned with a small number of real captured images. We further introduce a patch discriminator to supervise the network under novel views during fine-tuning, as well as a 3D color prior to improve synthesis quality. Our method can synthesize novel view images of a 360 surround of the scene with as few as 6 RGB-D images. Extensive experiments show the superiority of our method compared with the existing NeRF-based methods, including the approach that also aims to reduce the number of input images.
Paper
IEEE Version (Accepted by IEEE TPAMI)
Code
Video
|
|
BibTex
title={Neural radiance fields from sparse RGB-D images for high-quality view synthesis},
author={Yuan, Yu-Jie and Lai, Yu-Kun and Huang, Yi-Hua and Kobbelt, Leif and Gao, Lin},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
year={2022},
publisher={IEEE}
}
|
Last updated on March, 2023. |